“I am now able to laugh again, but I will never forget them,” said Ando, 57, who survived because she heeded official warnings to go inland before the storm hit.
Ten years on, the family’s mass grave is one of the few visible reminders of the devastation in Tacloban, the capital of Leyte province.
Tacloban bore the brunt of Haiyan’s fury and had to be rebuilt almost from scratch.
Now, it looks like any other Filipino city, with traffic-clogged streets and bustling restaurants.
An 18km (11-mile) seawall has been built along the coast to protect it against future storm surges.
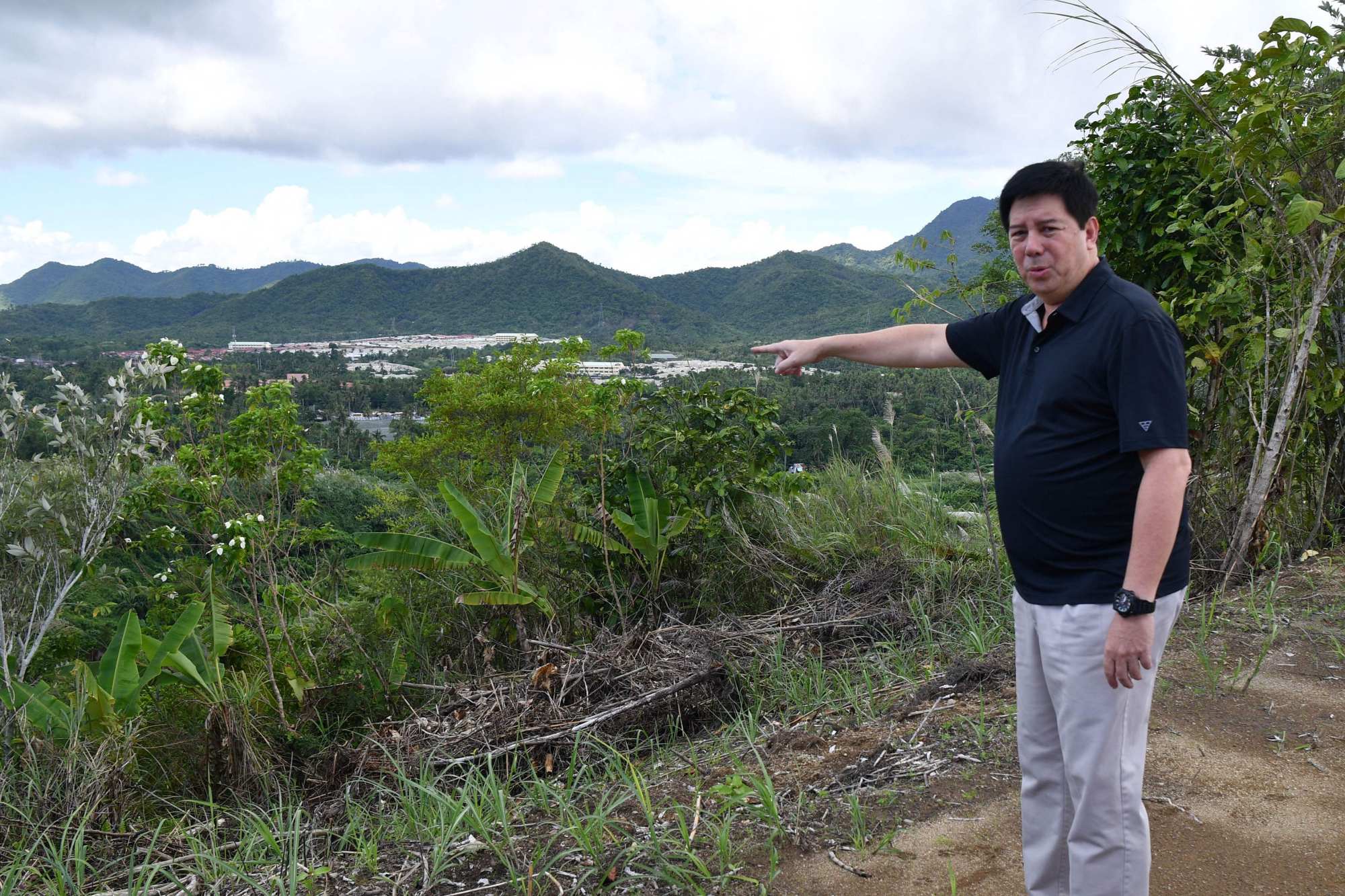

“I think we have fully recovered,” Mayor Alfred Romualdez said during a recent visit to the city of around 280,000 people.
As the Philippines prepares to commemorate the 10th anniversary of Haiyan, Romualdez said survivors had “moved on” from the disaster.
“But I don’t think they’ll ever forget,” he said.
Scientists have long warned that storms are becoming more powerful as the world becomes warmer because of human-driven climate change.
The Philippines, which typically endures more than 20 major storms a year, has plenty of experience dealing with disasters.
But that did not prepare the country for one of the strongest typhoons on record.

Haiyan unleashed winds of up to 315km an hour that flattened towns and cities across a 600km stretch of central islands.
Coastal houses and buildings thought safe enough to be used as evacuation centres on Leyte and Samar islands were swamped by storm surges up to five metres high.
About 6,300 people were killed and a decade later more than a thousand are still missing.
Over 4 million people were left homeless.
“I feel in terms of the national government, in terms of the local government, there were a lot of lessons learned,” Romualdez said. “But I would say that there are still many, many more lessons we still have to learn and we have to institutionalise.”
Since Haiyan, the country has invested in early warning systems, mass text messaging technology and public apps to identify potential dangerous areas, disaster and weather officials said.
Hazard maps used by government agencies are also updated regularly, weather alerts are issued earlier and in local languages, and pre-emptive evacuations are standard practice.
“The mindset has changed,” said Edgar Posadas, a director at the Office of Civil Defence in Manila.
Posadas said local governments now used their own funds, food packs and rescue personnel instead of relying on the national government, enabling them to respond to disasters more quickly.

The changes have been credited for lowering death tolls since Haiyan.
In December 2021, Super Typhoon Rai damaged or destroyed nearly twice as many houses as Haiyan, but the death toll was less than 500, UN and government data show.
“Experience really is the best teacher,” weather services chief Juanito Galang said.
Many of the people killed in Tacloban were living near the sea in flimsy shacks made of wood and corrugated iron sheets.
The government has since demolished many of the slum areas and moved around 14,000 families to relocation sites out of reach of storm surges.
While the concrete houses are safer than the shanties, some of the sites still lack running water.
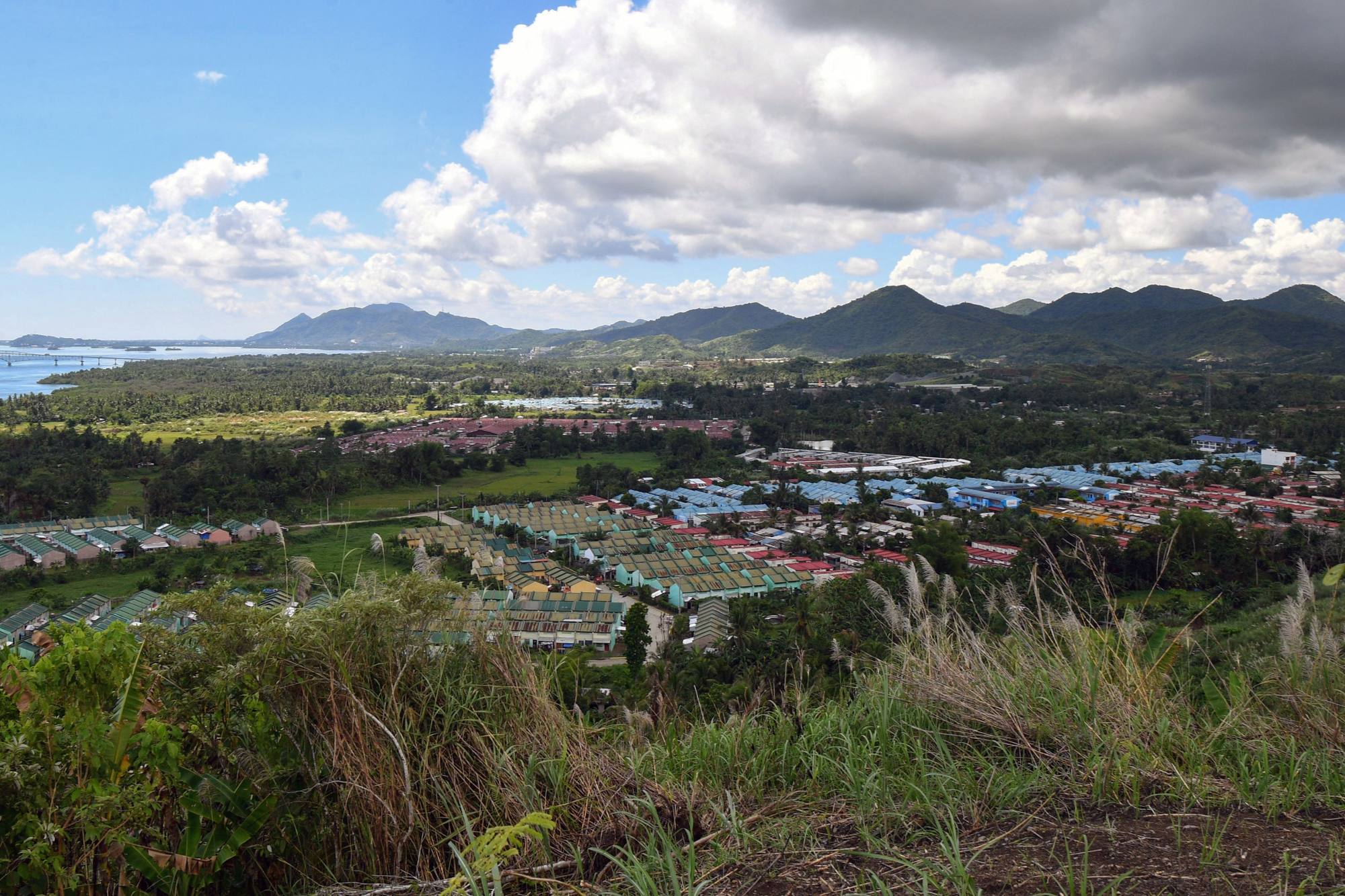

Rosie Boaquena, 63, moved to one 13km from downtown Tacloban, but two of her sons chose to stay in a one-room shack by the sea to be closer to their jobs.
“One of my sons sells fish, so he would need to leave [the relocation site] at midnight to pick up the fish, but there is no nighttime public transport,” she said.
Ando was also allocated a house in a hilly development, but she has not spent a single night there.
Instead, she rebuilt her house on the same plot of land near the sea where she has lived all her life and has many memories.

On Wednesday, Ando will mark the anniversary of Haiyan like she does every year, gathering family and neighbours near the mass grave to pray.
Six of her relatives are still missing, presumed dead, and one of her sons was left permanently disabled from the storm.
“We didn’t know what a storm surge was back then,” she said. “Now, whenever there’s a typhoon, we immediately evacuate.”

