The Ethereum network, which supports a sizable ecosystem of decentralized applications (dapps), has advanced significantly over the last couple of years.
Ethereum has been the pioneering force behind smart contracts, leading to ground-breaking innovations including DeFi), NFTs, the metaverse, and blockchain gaming. However, the rise in Ethereum’s popularity led to problems such as high costs, high energy consumption, and scalability. In this article, we’ll analyze Ethereum’s Roadmap to know how the future will be for this important blockchain.
A Journey of Upgrades
Ethereum’s developers devised a grand plan to address these problems. They called that plan “Ethereum 2.0,” which is a set of upgrades on the network. With these improvements, the network should become more resilient, scalable, safe, and effective for practical applications.
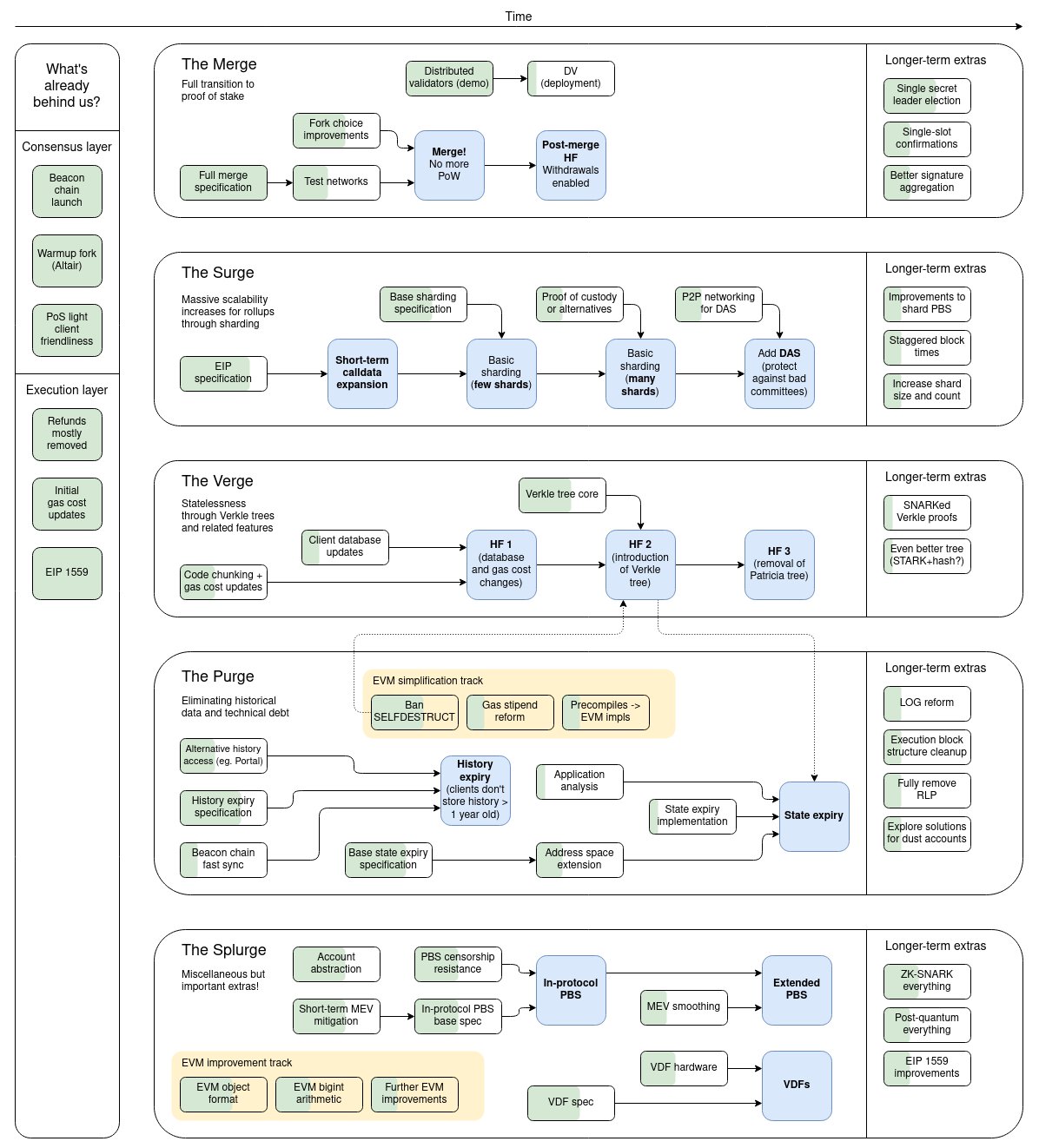
Source: Ethereum Roadmap
So, the changes in Ethereum 2.0 are intended to improve the performance of the Ethereum network in a number of areas. The adventure started in December 2020 with the Beacon Chain’s launch. This update in particular introduced the concept of the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to the network.
Ethereum’s developers didn’t stop there. They proceeded with other enhancements. Next on their list were the Berlin and London upgrades, which came in 2021. These upgrades optimized gas fees and introduced Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 (EIP-1559).
The merge
Ethereum merge merged the proof-of-stake testnet with the proof-of-work mainnet, converting the latter to PoS.
The merge finished on 15 September 2022. And the last merge-related upgrade (Shanghai-Capella) concluded last week.
— satvik.shm Ξ (@7vik_writes) April 17, 2023
Ethereum developers took things a notch higher in 2022 with the launch of the Gray Glacier, Bellatrix, and Paris upgrades—collectively referred to as “The Merge”. These effectively converted Ethereum from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS), where validators who staked ETH took over from miners as the source of blocks. Here are some of the benefits of the merger:
- Minimized energy consumption.
- Decreased the net issuance of ETH.
- Reduced block times (13.3s → 12s).
- It led to stronger finality.
- Introduced yield.
- Distributed Validator Technology(DVT). This resulted in better decentralization.
- Improved security.
Curious about what lies ahead for #Ethereum?
In our latest #Binance Research report, we take a closer look at Ethereum's roadmap, highlighting some of the key phases and upgrades worth keeping an eye on.
Read about them here
https://t.co/WNXegI1bhE
— Binance Research (@BinanceResearch) September 4, 2023
The Shanghai Upgrade.
The Shanghai Upgrade in April 2023 was the most recent Ethereum update. This upgrade, which also included EIP-4895, enabled ETH validators to unlock their network-staked ETH. It improved ETH liquidity since it enabled people to access staked ETH and related rewards.
Now let’s look at what Ethereum’s future looks like based on its roadmap.
The Surge
The surge intends to improve the Ethereum network’s scalability and decentralization. It features the implementation of EIP-4944, also known as Proto Danksharding. This will enable a new format of transaction via “data blobs” that can be seamlessly integrated into nodes and their processes.
The surge
The Ethereum surge is a set of upgrades that will increase the speed of the blockchain and its L2 counterparts.
This increase in scalability would solve the blockchain trilemma without compensating for network security.
The main upgrade here will be sharding:
— satvik.shm Ξ (@7vik_writes) April 17, 2023
The sharding method used by Ethereum divides transactions into numerous smaller batches, scaling the network horizontally, a process that is significantly simpler than enhancing a single machine.
For instance, it is more effective for 20 validators to validate five batches of 20 transactions each than it is for 100 validators to validate 1,000 transactions one at a time. Additionally, EIP-4844 establishes the foundation for transactions based on roll-up technology as well as resources that make it easier to create zero-knowledge scaling solutions. This phase will increase the scalability of the Ethereum network from 15 TPS to 100,000 TPS.
The Scrouge
The Scrouge upgrade seeks to prioritize decentralization and address protocol risks related to Maximum Extractable Value (MEV). It is the highest possible value that can be obtained from manipulating the order of transactions in a block above the recognized gas fees and block reward.
Many in #DePin space have suggested the future will be nodes run from mob devices. @VitalikButerin advocating stateless clients to unlock this. End result is more decentralisation. This is what the future internet looks like and why we are building #Web3https://t.co/0AseX6hcEg
— marklittle.eth (@mark_little2) September 6, 2023
One of the ways to tackle this MEV issue is through the implementation of PBS (Proposer Builder Separation). PBS addresses the centralization risk posed by MEV and also offers an anti-censorship solution
The Verge
According to Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin, the Verge will reduce the amount of data validators store on their machines. It will accomplish this by introducing Verkle trees. Buterin claims this is an improvement over Merkle proofs that enables substantially reduced proof sizes.
Vitalik Buterin believes that future upgrades to Ethereum could allow full nodes to run on mobile devices, making the network more decentralized. #Ethereum #VitalikButerin #mobile #decentralization
— CubeCoin | News (@CubeCoinCrypto) September 7, 2023
The Verkle trees are one component of a larger roadmap for making Ethereum stateless, a difficult idea that is still being developed. In simple terms, the proposal seeks to establish stateless clients, in which validating nodes don’t need to store state data before block verification.
The Purge
The Purge upgrade contains a number of improvements to get rid of outdated network history and gradually clean up the network. It will minimize Ethereum’s technical debt and historical data storage requirements. This will reduce the storage requirements for node operators.
The Purge also plans to introduce history expiration (EIP-4444), which will allow some node operators to skip storing some of the data from earlier blocks. Validators will simply store one year’s worth of history rather than the entire blockchain’s history.
EIP-4444 also aims to remove excessive or unneeded functions from the Ethereum Virtual Machine, optimize the protocol, minimize technical complexity, and lower the cost of participating in the network. The major objective is to reduce network traffic and increase transaction speed.
The Splurge
The Splurge upgrade, which is the final stage, is intended to solve all outstanding issues in the network. This upgrade will only be used for research and to guarantee the proper execution and implementation of previous processes.
very concerned about what will happen after the Ethereum Merge, Surge, and Verge because then we're just left with rhymes like the Purge, Scourge, or Dirge pic.twitter.com/z2INpfQ9UN
— Molly White (@molly0xFFF) September 17, 2022
The phases contained in Ethereum’s roadmap will improve the network once they each go live. They will also lead to more liquidity and earning opportunities. However, these upgrades could possibly affect the price of ETH. But we can’t say in what direction that will happen. Instead, it will depend on several factors, including market trends.
– For more cryptocurrency news, check out the Altcoin Buzz YouTube channel.
– Unlock the key to managing your crypto portfolio like a PRO! Our top analysts bring you exclusive insights and the latest updates on cryptocurrency trading. Join Altcoin Buzz Alpha on Youtube or Patreon for just $15/month!
The post What is the Future of Ethereum? We Analyze its Roadmap appeared first on Altcoin Buzz.

